About This Condition

What Is It?
A bunion is a deformity of the bone at the base and side of the big toe, where there is an enlargement of the metatarsopholangeal joint (say that three times fast). Bunions occur when the toe moves out of its normal placement. The subsequent enlargement and its protuberance lead to pressure and friction as rubbing against footwear occurs. As time progresses, the angle of the big toe will be inward toward the other toes. In some instances, the big toe overlaps a third toe – this is called Hallux Valgus. As the enlargement or proturberance gets larger and larger, it cauess more inflammation and / or irritation. Sometimes, the big toe will move toward the second toe, rotating and / or twisting in the process. This is known as Hallus Abducto Valgus. Other toe deformities may come as a result of bunions, including hammertoe.
Those with bunions often suffer from pain and discomfort due to the constant friction, irritation, and rubbing against their shoes. Skin over the toe may also become tender and red. Since this joint is always flexing as steps are taken, the larger the bunion gets, the more painful walking becomes. In the later stages, bursitis or arthritis may occur, skin on the bottom of the foot has the potential to become thicker, and day-to-day walking may become increasingly difficult. All of these factors contribute to chronic pain.
Causes
The leading cause of bunions? Wearing shoes that are too tight. Bunions tend to run in families even though they are not hereditary – this is typically due to the foot structure. Other causes of bunions include neuromuscular problems, flat feet, pronated feet, and foot injuries. In Western countries, bunions occur in around 33% of the population.
Treatment
Unfortunately, bunions cannot fix themselves as they are a bone deformity. When treating bunions, it is important to both relieve the pain / pressure and to stop progressive growth of the bunion. The common methods of treatment are:
- Removing calluses and corns on the foot.
- Begin wearing footwear that is carefully-fitted and designed to be accommodating to the bunion.
- Maintain joint mobility through exercises. This is to avoid arthritis and stiffness down the
road. - Wear protective padding to reduce or eliminate friction. This padding is typically made of
felt material. - Wearing splints to help the joints align properly – usually worn at nighttime. This
recommendation is most common for adolescents who have bunions, as their bone
development is still young and can potentially adapt.
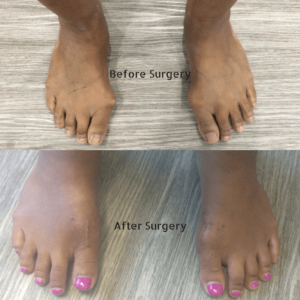
For more serious and advanced cases of bunions, conservative treatments are not always adequate in preventing progressive damage. In instances such as these, a bunionectomy (bunion surgery), may be recommended to help remove the bunion altogether and bring alignment back into the toe.